USB Block Review 2025: The Fastest Way To Block Unauthorized USB Devices On Windows 10 and Windows 11
The short answer
If you need to block USB drives on Windows 10 or Windows 11, allow only your approved devices, require a password prompt for USB storage, and log every attempt, USB Block is the cleanest oneinstall solution. It lets you whitelist your own flash drives and phones while blocking all other USB mass storage, external HDDs/SSDs, SD cards, CD/DVD, network mapped drives, and even nonsystem partitions. It includes stealth mode, Safe Mode protection, and hack attempt logs. Pricing on NewSoftwares’ store https://www.newsoftwares.net/ shows USB Block onetime license at 49.95 USD as of today.
Below you’ll find every workable way to block USB access on Windows, with stepbystep tutorials, plus troubleshooting. If you’re short on time, start with Method 1.
What this review covers
- A complete, working tutorial for USB Block
- Builtin Windows methods with exact paths and options
- BitLocker policies that allow read but block write
- Whitelisting only approved USBs by VID/PID or device IDs
- Auditing and USB access logs
- Fixes when policies don’t apply or get overridden
- A quick comparison with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Device Control, CoSoSys Endpoint Protector, and GiliSoft USB Lock
Why USB blocking still matters in 2025
Regulators and frameworks expect removablemedia controls. NIST SP 80053 MP7 Media Use calls for restricting removable media like flash drives; many orgs map this to technical controls such as USB blocking or allowlists.
Windows gives you policies, but they can be brittle across builds or require Intune or Defender for Endpoint. A dedicated tool like USB Block reduces moving parts on standalone PCs and small fleets while still giving you logging and whitelisting.
Method 1 USB Block by NewSoftwares: block everything, allow only what you trust

What USB Block does
- Blocks USB storage, external HDD/SSD, memory cards, mobile devices that expose storage, CD/DVD, Bluray, nonsystem partitions, and network mapped drives
- Prompts for a password on unauthorized media; authorize once to add to your allowlist
- Stealth mode, Safe Mode protection, hackattempt logging, and an Authorize List for trusted devices
Quick install and firstrun setup
- Download and install USB Block. Launch it.
- Set a strong master password. Keep it in your enterprise password manager.
- Open the Control Center. By default, USB devices are blocked. You can toggle categories like Block Discs/Floppy, Block Network Access, or Block NonSystem Drives depending on policy.
How to whitelist your own flash drive or phone
- Insert your own drive. USB Block shows a password prompt.
- Enter your password and check Remember (add to Authorize List).
- The device is now trusted; future use won’t prompt. You can manage or remove it later from Authorized Devices.
How to block network mapped drives (stop “copy to \server\share”)
- In Control Center, check Block Network Access.
- This blocks network mapped drives and direct access by path or IP from that computer.
- Add exceptions by authorizing the target if allowed by policy.
How to block CD/DVD and other media
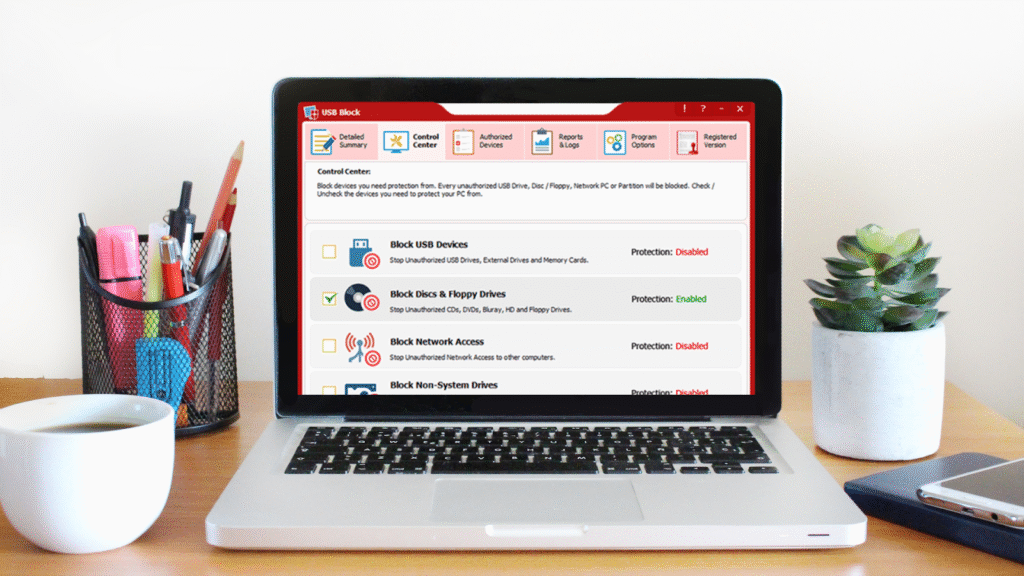
- In Control Center, check Block Discs/Floppy.
- Inserting a disc will now show a password prompt.
- To trust a specific disc, authorize it once.
How to block nonsystem partitions
- Check Block NonSystem Drives.
- Only the Windows system drive remains accessible without authorization.
Security extras to switch on
- Stealth mode hides the app from Start, Programs, and Add/Remove; launch via your chosen hotkey.
- Safe Mode protection keeps blocks active during Safe Mode.
- Hack attempt monitoring logs bad passwords and uninstall tries with time and user.
Why USB Block is the best fit for many SMB and singlePC cases
- Covers more than USB out of the box, including nonsystem partitions and network mapped drives, which plug gaps that Group Policy leaves open on standalone PCs.
- Userfriendly allowlist workflow with password prompts keeps admin overhead low.
- Stealth and Safe Mode enforcement reduces insider workarounds.
- Onetime license and no backend required, unlike many enterprise DLP suites.
Method 2 Windows Group Policy: deny read, write, or execute on removable storage
Works well on Pro/Enterprise editions joined to AD or managed locally.
Deny read or write on USB drives
- Open Group Policy Editor or GPMC.
- Path: Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access
- Path: Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access
- Enable Removable Disks: Deny read access to block reading.
- Enable Removable Disks: Deny write access to block writing but allow read.
- Optionally set Deny execute access.
- Apply to the target OU or computer.
You can also scope this per user under User Configuration using the same Removable Storage settings.
Pros
- Native and fast to deploy in AD.
- Can block write but allow read to support certain workflows.
Cons and 2025 caveat
- Some admins reported RemovableStorageDevice GPO broke after April 2025 updates, with Microsoft acknowledging an issue and working on a fix. Test before broad rollout.
Method 3 “Allow only approved USB drives” using Device Installation Restrictions
This approach prevents installation of nonapproved USB storage while allowing keyboards and mice. It’s precise but requires you to collect device instance IDs or setup class GUIDs for the devices you allow or block.
Steps
- Open Group Policy.
Path: Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Device Installation > Device Installation Restrictions. - Enable Prevent installation of devices not described by other policy settings.
- Enable Allow installation of devices that match any of these device IDs and click Show.
- Add the device instance IDs for your approved USB drives.
- Optionally enable Prevent installation of devices using drivers that match these device setup classes to block all USB storage class while allowing HIDs.
- Update policy and test.
Why keyboards and mice still work
You’re targeting storage device class or specific device IDs. Human Interface Devices use different classes and won’t be blocked by the storage policy.
Where this shines
- You want zero trust removable media and will whitelist only company drives.
- You don’t want to break HIDs or webcams.
Method 4 BitLocker policy: allow read, block write unless the drive is encrypted
If you must let people read files but want to block writing to USB unless it’s BitLockerprotected, use this.
Steps
- Open Group Policy.
Path: Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Removable Data Drives. - Enable Deny write access to removable drives not protected by BitLocker.
- Optionally configure the Allowed identification field for orgtagged drives.
Notes
- If Removable Disks: Deny write access is enabled in Removable Storage Access, it overrides BitLocker CSP for write access. Be aware of interactions.
Method 5 Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Device Control with Intune
For organizations on MDE P1/P2 or Defender for Business, Device Control gives rich policies across Windows and more. You can block by vendor ID and product ID (VID/PID), serial number, hardware ID, and define read/write/execute/print masks.
Fast path in Intune
- Create Device Control policy for Removable storage access control.
- Build Reusable settings for allowed media with VID/PID or serial numbers.
- Add block all removable media rule, then add allow rules for your reusable settings.
- Assign to pilot group, then expand.
Why choose this
- Need centralized reporting, peruser/pergroup targeting, and finegrained VID/PID control.
- Integrates with Intune and Defender dashboards.
Method 6 Registry and driver methods
USBSTOR service toggle
Setting HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR\Start to 4 disables the USB storage driver. Set it back to 3 to reenable. This is coarse and can be reverted when a new device is installed if not combined with install restrictions.
Usbstor.inf/.pnf permissions
Denying SYSTEM and users read permission on usbstor.inf/.pnf stops driver installation for storage devices. This is an older Microsoftdocumented method that still works in niche cases.
Reality check: both are brittle compared to the policybased approaches above. Use only if you can’t deploy GPO or Intune and you accept the tradeoffs.
Method 7 BIOS/UEFI port disable
Many business PCs let you disable ports in firmware. This can be effective in labs or kiosks but is hard to manage at scale and easy to reset if not locked with BIOS passwords. Prefer OSlevel control for manageability.
Activity logs: how to monitor and prove USB controls
Windows native audit
Enable Advanced Audit Policy: Audit Removable Storage to log access attempts on removable media. Look for Event ID 4663 (object access) and 4656 (handle requested).
Defender Device Control logging
MDE shows Device Control events in reports; Intune policy XML includes access masks and controlled IDs for compliance evidence.
USB Block logs
USB Block records invalid password, uninstall attempts, and other hack attempts with time/user. This is useful for insider risk reviews on unmanaged or lightly managed PCs.
Tutorials you can copypaste today
A. Block USB on one PC in minutes with USB Block
- Install USB Block and set a password.
- Open Control Center. Confirm Block USB Devices is checked.
- Optional: check Block Discs/Floppy, Block Network Access, Block NonSystem Drives.
- Insert a company USB drive, enter the password, and check Remember to whitelist it.
- Switch on Stealth mode and add a hotkey if you want to hide the app.
B. Block write, allow read with Group Policy
- Open GPMC, edit a GPO linked to the target OU.
- Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
- Enable Removable Disks: Deny write access.
- Update policy and test with a nonapproved drive.
C. Allow only approved USB drives on Windows 11
- Collect device instance IDs for approved drives from Device Manager.
- In GPO, enable Prevent installation of devices not described by other policy settings.
- Enable Allow installation of devices that match any of these device IDs, click Show, and add your IDs.
- Optionally block by setup class for USB storage.
- Update policy and test.
D. Require BitLocker before writing to USB
- GPO path: BitLocker Drive Encryption > Removable Data Drives.
- Enable Deny write access to removable drives not protected by BitLocker.
- Optionally set Allowed identification field for your corporate USBs.
E. Intune and Defender Device Control VID/PID allowlist
- In Intune, create Device Control policy for Removable storage.
- Add block all removable media rule.
- Create Reusable settings for your drives using VID/PID and serials, then add allow rules.
- Assign to a pilot group and monitor reports.
F. Oldschool registry toggle for USBSTOR
- regedit to HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR.
- Set Start=4 to disable or Start=3 to enable.
- Reboot. Pair with install restrictions or INF permission block to prevent reenable on first new device.
Troubleshooting: specific fixes that save hours
USB Block issues
- No password prompt appears
Confirm the category is blocked in Control Center. If another DLP tool is installed, resolve conflicts by keeping one control layer active. - Authorized device still asks for password
Reinsert, enter password, ensure Remember is checked; verify the device appears in Authorized Devices. - Users found the app
Turn on Stealth mode and a hotkey. - Safe Mode bypass
USB Block enforces in Safe Mode. Confirm Safe Mode protection is enabled in options.
Group Policy issues
- Policy not applying
Check the exact path and whether you configured Computer vs User policy. Refresh with gpupdate /force. Verify the target OU and security filtering. - After April 2025 updates, deny rules stopped
There is a known issue with RemovableStorageDevice blocking via GPO. Validate build dependencies or use Device Installation Restrictions or MDE Device Control as a fallback. - Users can still write
If BitLocker policy is present, ensure User Configuration > Removable Storage Access isn’t overriding it.
Intune and Defender Device Control
- Allowed drive still blocked
Confirm VID/PID or serial number is correct and present in Reusable settings. Some devices expose multiple IDs; include all relevant IDs. - Policy says applied but behavior unchanged
Validate access mask values for Read/Write/Execute/Print in your XML. Start with a pilot and check MDE Device Control reports.
Registry method
- USBSTOR Start reverts to 3
This happens when a new device installs the driver. Combine with INF/PNF permission deny or switch to Device Installation Restrictions.
Logging and audit
- No USB access events
Enable Audit Removable Storage and monitor Security log for 4663/4656. Some environments also require setting HotplugSecureOpen for consistent events.
Windows vs dedicated software vs full DLP: what to pick
Quick matrix
| Need | USB Block | Group Policy (RSA/Device Install) | BitLocker policy | Defender Device Control | Endpoint Protector |
| Block all removable storage | Yes | Yes | Write only | Yes | Yes |
| Allow only approved USBs | Yes with Authorize List | Yes by device IDs | No | Yes by VID/PID/serial | Yes |
| Password prompt for USB access | Yes | No | BitLocker password on protected drives only | No | Optional controls |
| Block CD/DVD and nonsystem drives | Yes | Yes for CD/DVD via RSA | No | Yes | Yes |
| Block network mapped drives | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Stealth and Safe Mode protection | Yes | No | No | No | N/A |
| Centralized reporting | Basic logs | Event logs | Event logs | Rich in MDE | Full console |
| Best for | Standalone PCs, SMB | ADjoined devices | Require encrypted USBs | Intune managed fleets | Crossplatform DLP |
USB Block covers more local exfil paths in one UI and is effortless to roll out on a handful of machines. MDE or Endpoint Protector win on centralization at scale but take longer to plan and maintain.
A few realworld patterns that work
- NYC professional services firm that lets partners carry case files on named, encrypted USBs sets BitLocker “deny write unless encrypted” and adds Device Installation Restrictions allowlist for firmissued drives. Local kiosks run USB Block for extra coverage on disc burning and nonsystem partitions.
- Retail locations without AD or Intune install USB Block only, whitelisting store manager drives and blocking network mapped drives on cashwrap PCs to stop casual copying.
- Healthcare teams reference MP7 style controls and removable media handling to support HIPAA security rule practices.
How to check USB access logs fast
Windows Security log
- Turn on Audit Removable Storage. Filter for Event 4663 with Object Name on removable paths.
Defender for Endpoint
- Use Device Control reports to see blocked/allowed decisions by VID/PID and policy.
USB Block
- Open USB Block and review Hack Attempt Monitoring to find invalid password or uninstall attempts with timestamp and user.
USB Block vs Endpoint Protector vs GiliSoft USB Lock
- USB Block focuses on local endpoint exfil control with strong coverage of storage classes, nonsystem partitions, and network mapped drives, plus stealth/Safe Mode.
- Endpoint Protector is a full DLP suite with centralized console and crossplatform support, including a Device Control module for granular USB permissions. Great at scale, heavier to deploy.
- GiliSoft USB Lock is comparable in purpose, with whitelists and CD/DVD controls; it’s another viable singlePC option if you’re comparing tools.
Why “USB Block” is the best choice for most busy teams
- Fastest path to results on unmanaged or lightly managed Windows PCs with password prompts, whitelisting, and logs in one place.
- Wider coverage than simple GPO deny rules, including network mapped drives and nonsystem partitions that many forget to restrict.
- Resilient features like Stealth and Safe Mode protection cut down on insider workarounds.
- Cost predictable onetime license without servers or Intune dependency.
FAQ
- How do I block USB drives but still allow keyboards and mice on Windows 11?
Use Device Installation Restrictions to block storage classes or nonapproved device IDs. HIDs are different classes and remain unaffected. - Can I allow only companyapproved USB drives?
Yes. On a single PC, whitelist with USB Block. In AD or Intune, use Allow installation of devices that match these device IDs or MDE VID/PID allow rules. - I want readonly USB access. What’s the easiest way?
Enable Removable Disks: Deny write access in Group Policy. Or use BitLocker policy to require encryption before writes. - How do I block CD/DVD burning too?
USB Block can block discs with a checkbox. Natively, set CD and DVD: Deny read and Deny write in Removable Storage Access. - How do I log USB usage and see who tried to copy files?
Enable Audit Removable Storage. Review Security events like 4663 and 4656. USB Block also logs hack attempts. - Group Policy isn’t blocking after updates. What now?
There’s a known 2025 issue with RemovableStorageDevice blocking via GPO. Use Device Installation Restrictions, BitLocker writedeny, or MDE Device Control as a workaround until patched. - Is the registry USBSTOR method safe?
It’s crude and can be undone when new drivers install. Pair it with INF/PNF permission blocks or prefer policybased methods. - Can I require a password before any USB drive works?
Windows doesn’t natively prompt for a password for all drives. USB Block does this for unauthorized devices. BitLocker To Go prompts only for drives that are encrypted. - How do I block USB without touching BIOS?
Use Removable Storage Access, Device Installation Restrictions, BitLocker policy, or USB Block. All are OSlevel. - How do I unblock USB ports if they were locked?
- GPO: set deny policies to Not Configured and update.
- BitLocker writedeny: set to Disabled.
- Registry: set USBSTOR Start=3.
- Can I block write to USB but still let a USB scanner or printer work?
Yes. Block storage classes while allowing other device classes, or allow by hardware ID. MDE Device Control is strongest for complex mixes. - What about compliance like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS?
Controls like NIST MP7 encourage restricting removable media. Many orgs combine USB blocking with encryption and audit to meet policy requirements. - How do I check which USBs are approved in Intune?
Review your Reusable settings and the assigned Removable Storage Access Control policy. Crosscheck VID/PID and serials from Device Manager. - What if I need copy protection, not just blocking?
Blocking stops exfil via ports. To copyprotect media you distribute, NewSoftwares’ Copy Protect is built to prevent duplication of your own content. Different goal from USB blocking. - How does USB Block compare to Endpoint Protector or Defender?
USB Block is fastest on individual PCs and covers network mapped drives and nonsystem partitions. Defender and Endpoint Protector excel in central management and reporting across large fleets.
Final recommendation
If you’re in a hurry and need results on Windows today, install USB Block, turn on the categories you care about, and whitelist your approved devices. It’s the fastest way to get antidata theft controls, password prompts, and activity logs without wrestling with AD or Intune. When you later need centralized policy and fleet reporting, add Defender Device Control or Endpoint Protector on top. read mora






